🌟 Rare Fungal Infections in the Ear Canal: A Hidden Danger 🎧🦠
🧠 Introduction: The Mystery of the Itchy Ear
Rare Fungal Infections in the Ear Canal: The human ear is an incredibly intricate structure 🌀 that helps us hear, maintain balance, and interact with the world. While we regularly take our ears without any consideration, they can grow to be host to a variety of well being issues — together with fungal infections.
Among the numerous lesser-known conditions is otomycosis — a fungal infection that impacts the external auditory canal (the outer section of the ear). Whereas widespread kinds of otomycosis happen incessantly in tropical climates 🌴, rare fungal infections in the ear canal are sometimes extra dangerous, elusive, and challenging to diagnose. 😟
This text delves deep into the causes, symptoms, varieties, analysis, therapy, and prevention of those unusual fungal invaders. Get able to uncover a lesser-known medical thriller that could possibly be hiding behind that annoying itch in your ear. 👂🔬
👂 Anatomy of the Ear Canal: A Quick Overview
To know how fungal infections have an effect on the ear, it helps to know a bit in regards to the ear’s construction. 🧏
🧩 Three Elements of the Ear:
-
Outer Ear (Exterior Ear) – Contains the pinna (the seen half) and the ear canal
-
Center Ear – Accommodates tiny bones (ossicles)
-
Interior Ear – Controls stability and listening to 🌀
Fungal infections nearly at all times have an effect on the exterior ear canal, however in extreme circumstances (particularly uncommon fungi), the an infection could invade deeper tissues. 😬
📌 Part 1: Understanding Fungal Infections within the Ear
🌡️ What Is Otomycosis?
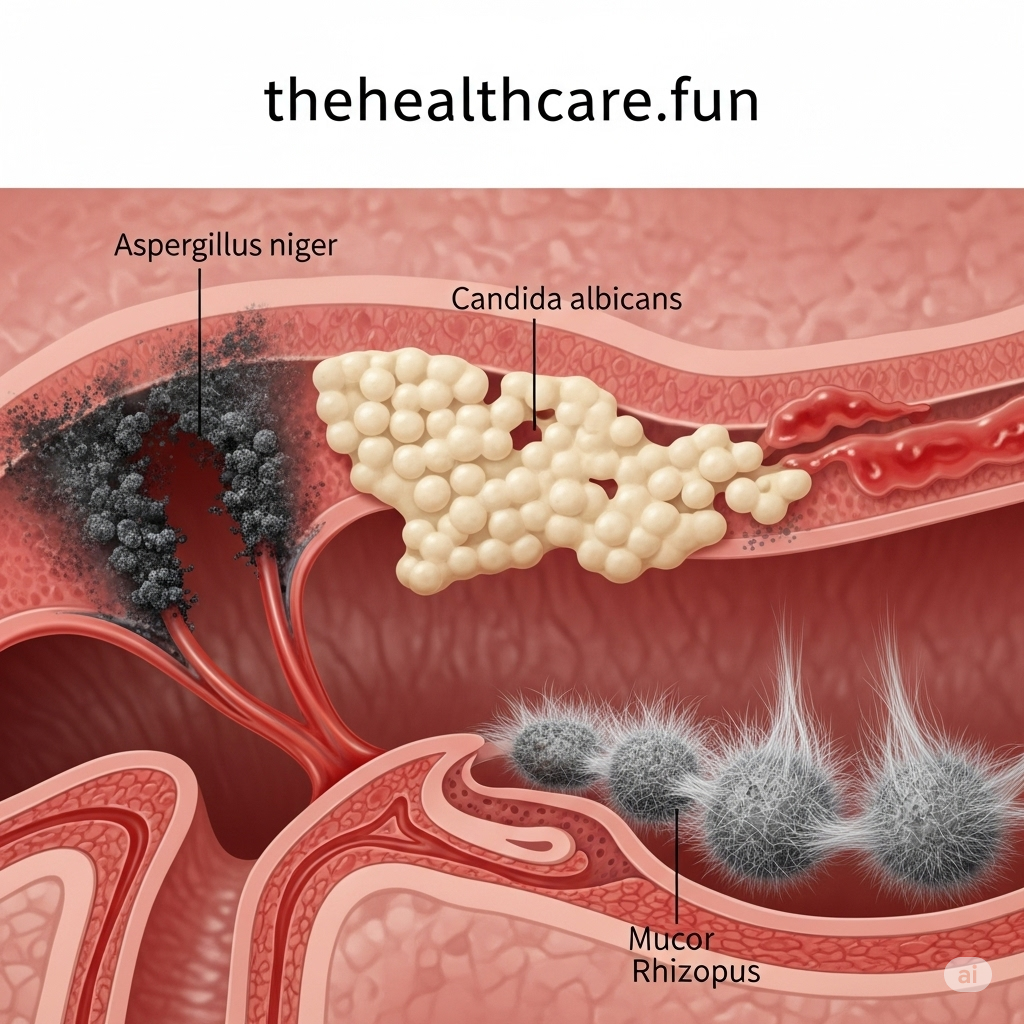
Otomycosis is a fungal an infection of the exterior ear canal, which may have an effect on one or each ears. Most circumstances are attributable to widespread fungi like Aspergillus or Candida, however in uncommon situations, extra aggressive and unusual fungi are accountable. 😬
These uncommon fungal infections could pose a higher menace as a result of they:
- Are proof against frequent antifungal drugs 💊
- Occur in immunocompromised patients 🤒
- Can invade deeper tissues of the ear 😱
- Typically mimic bacterial infections, delaying analysis ⏳🧫 Frequent vs. Rare Fungi
| Sort | Frequent Fungi 🧹 | Uncommon Fungi 🚫 |
|---|---|---|
| Names | Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans | Scedosporium apiospermum, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor |
| Occurrence | Typically in tropical/humid regions 🌴 | Usually linked to immunocompromised sufferers or contaminated environments 🧪 |
| Remedy | Topical antifungals | Systemic antifungals, surgery could also be needed 🏥 |
🔍 Part 2: Causes of Rare Fungal Infections in the Ear Canal
Understanding the triggers of those infections is essential to prevention and early treatment. Let’s explore what causes rare fungi to invade the ear. 🔎
1. 🧪 Exposure to Contaminated Water
Engaging in swimming 🏊♂️ within contaminated lakes or rivers, particularly in tropical or subtropical regions, may subject your ear to uncommon fungi present in soil and water.
2. 🏥 Hospital-Related Exposure
Patients with long hospital stays, especially these in ICUs, can develop hospital-acquired fungal infections by means of units like catheters or during surgeries. Occasionally, fungi can travel to the ears through systemic spread. 🏨
3. 🚫 Overuse of Antibiotics or Steroids
Overuse of antibiotic ear drops or steroids may disturb the natural flora of the ear and encourage the proliferation of fungi — including uncommon and resistant strains. 💉
4. 🧬 Weakened Immune System
People with the following situations are at higher danger:
- HIV/AIDS 🧬
- Cancer patients on chemotherapy 🎗️
- Organ transplant recipients 🫀
- Diabetics with poor control 🍭
- Autoimmune issues 🧠
🚨 Section 3: Symptoms of Rare Fungal Ear Infections
Rare fungal infections don’t all the time present the same approach as frequent ones. They might be extra extreme, continual, or aggressive. Look out for these indicators:
🔊 Common Symptoms
- Intense itching 😖
- Discharge (may be yellow, white, black, or green) 🟡⚫
- Fullness or stress in the ear 🧱
- Pain or discomfort 🩹
- Decreased hearing 🔇
🚨 Advanced or Dangerous Signs
- Swelling of the ear canal 😷
- Spread to the middle or interior ear 🧠
- Fever or malaise 🤒
- Foul smell from the ear 💀
- Bleeding or ulceration 🚨
🧬 Section 4: Rare Fungi That Infect the Ear Canal
Listed below are a number of the much less widespread fungal brokers which were recognized to trigger harmful ear infections:
🧫 1. Scedosporium apiospermum
- Found in soil and stagnant water 💧
- Could cause persistent otitis externa
- Immune to many antifungals ⚠️
- May lead to invasive brain infections in immunocompromised individuals 🧠
🧫 2. Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Usually causes lung infections
- May spread to ear canal through bloodstream
- Endemic in components of North America 🌎
🧫 3. Histoplasma capsulatum
- Typically linked to bat droppings or fowl feces 🦇🕊️
- May cause systemic histoplasmosis, sometimes reaching the ear
🧫 4. Mucor species
- Causes mucormycosis, a life-threatening fungal infection
- Regularly affects diabetics
- Can invade sinuses, brain, and ears 😱
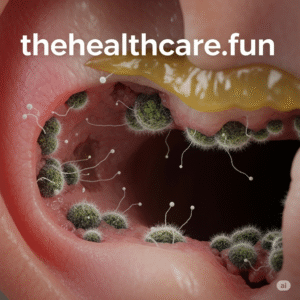
🧪 Section 5: Diagnosis of Rare Fungal Ear Infections
Accurate diagnosis is essential to treating these hidden invaders. Here’s how medical doctors work out what’s going on:
🏥 1. Physical Examination
- ENT specialists use an otoscope to inspect the canal
- Black, green, or yellow fungal debris might be visible 🎥
🔬 2. Fungal Culture and Microscopy
- A sample of discharge is taken and examined beneath a microscope 🧫
- Cultured in a lab to establish the particular fungus 🧪
🧬 3. Imaging Checks
- CT or MRI scans may be needed if:
- Infection spreads beyond the ear 🧠
- Brain abscess or bone invasion is suspected 💣
🧫 4. Blood Checks
- For systemic fungal infections, antibody or antigen exams can detect pathogens within the bloodstream 🔍
💊 Section 6: Therapy Strategies for Rare Fungal Ear Infections
👂 1. Ear Cleaning (Aural Toilet)
- The ENT specialist manually removes fungal debris 🧼
- Generally completed multiple occasions for thorough debridement 🌀
💊 2. Topical Antifungals
- Clotrimazole, Miconazole, or Econazole may be used initially
- Effectiveness will depend on fungus kind and extent of infection
💉 3. Systemic Antifungals
- Rare fungi usually require oral or IV drugs similar to:
- Voriconazole 💊
- Amphotericin B (for mucormycosis) 💉
- Itraconazole 📦
- Therapy might last several weeks or months ⏳
🛠️ 4. Surgical procedure
- In severe instances where infection spreads to bone or brain:
- Surgical debridement or mastoidectomy could also be vital 🔪
- Elimination of necrotic tissue to forestall unfold ⚔️
🚷 5. Avoid Self-Remedy
- Home remedies or cotton swabs 🚫 could potentially worsen the condition
- At all times consult an ENT specialist for proper evaluation 👨⚕️
🛡️ Section 7: Prevention Suggestions 🌟
🚿 1. Maintain Ears Dry
- Avoid inserting water in ears during shower or swimming 🧼
- Utilize ear plugs when swimming in lakes or public swimming pools 🏊♀️
👂 2. Avoid Inserting Objects
- No cotton swabs, hairpins, or fingers! 🚫👆
- These may cause scratches on the skin and permit fungi to infiltrate.
🧴 3. Use Ear Drops Correctly
- Avoid long-term use of antibiotic or steroid drops until prescribed 🎯
🧑⚕️ 4. Regular Checkups for High–Danger Groups
- You probably have diabetes, most cancers, or immune deficiency:
- Schedule common ENT evaluations 👩⚕️
- Report any ear discomfort instantly ⚠️
🧠 Part 8: Case Research – Actual Life Fungal Infections in the Ear Canal
📖 Case 1: Mucormycosis in a Diabetic Affected person
A 52-year-old man with uncontrolled diabetes complained of ear ache and swelling. Preliminary prognosis urged a bacterial an infection, however cultures revealed Mucor. He underwent surgical debridement and was handled with IV Amphotericin B. Restoration took 6 weeks however was profitable. 💪
📖 Case 2: Scedosporium An infection in a Swimmer
A 19-year-old athlete experienced persistent ear discharge following swimming in a polluted river. Preliminary remedies failed till Scedosporium apiospermum was recognized. He responded nicely to Voriconazole remedy. 🏊♂️
🧭 Part 9: Residing with Fungal Ear Circumstances
Residing with continual or uncommon ear infections might be irritating. 😔 Here is learn how to cope:
🧘 1. Keep Ear Hygiene
- Use a comfortable fabric for outer ear cleansing solely 🧼
🌬️ 2. Let Your Ears Breathe
- Keep away from headphones for prolonged durations 🎧
- Keep airflow to forestall moisture buildup 🌬️
📅 3. Comply with Up Diligently
- Full your remedy course ⏳
- Go for repeat fungal cultures if signs persist 🔁
📚 Conclusion: Ear Well being Issues! 🎉👂
Although uncommon fungal infections within the ear canal is probably not widespread, they’re definitely severe and require immediate consideration. 🛎️ Whether or not you’re an outside fanatic, immunocompromised affected person, or simply somebody who loves utilizing earbuds — you want to pay attention to these stealthy fungal attackers.
By understanding the signs, causes, prognosis, remedy, and prevention, you empower your self with the data to act early and keep protected. 🚨
So the following time your ear feels itchy, full, or painful — don’t ignore it. That tickle would possibly simply be one thing way more severe than you suppose. 🦠🕵️♂️
📬 Have Questions?
Be at liberty to ask a healthcare supplier, or contact your native ENT clinic in the event you discover persistent ear signs.
✅ Keep knowledgeable, keep wholesome, and at all times hearken to your ears! 👂💖